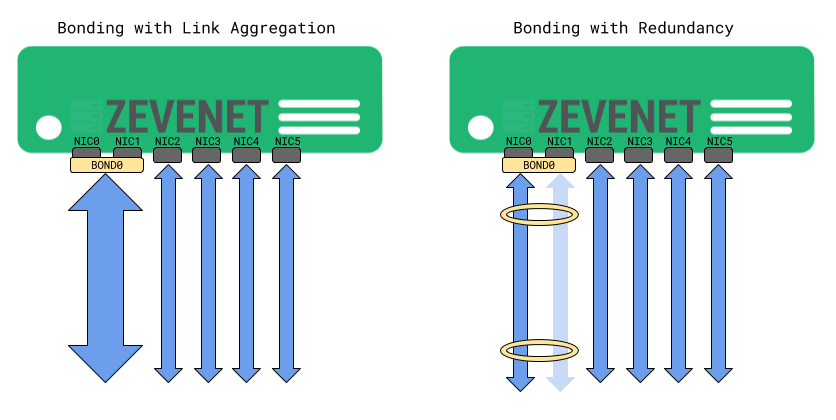
Bonding interfaces (also known as link bundling, port trunking, channel bonding, link aggregation, NIC teaming, etc) allow the connection of several physical network interfaces to work as one logical network interface. This interface adds load balancing between several NIC layers. The redundancy also allows failover between those NICs that build the bonding.
See below an example of two different use cases of the bonding configurations.
This section describes how to configure and operate the bonding interfaces.
Bonding Interfaces List #
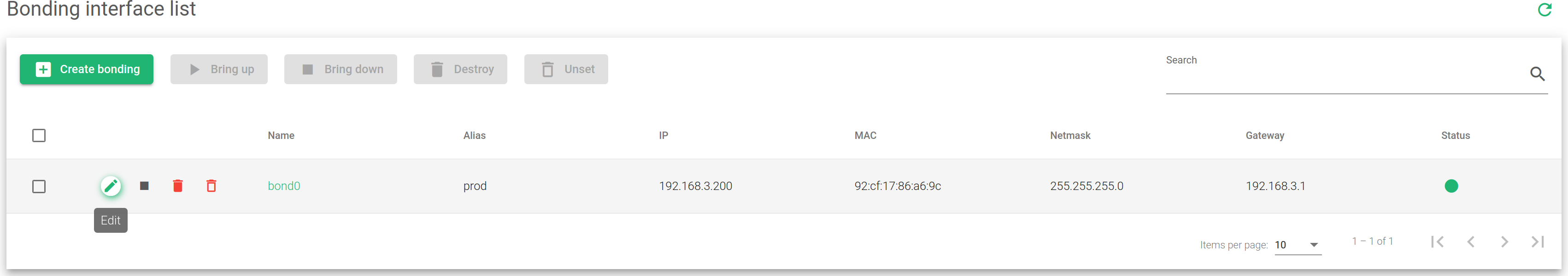
This table lists all the bonding network interfaces configured in the system.
Actions available for the selected interfaces:
Create bonding. This option redirects to the bonding interface creation form.
Bring up. Starts the selected interfaces and configures them to the accept traffic.
Bring down. Shuts down the selected interfaces and stops accepting traffic.
Destroy. Removes the Bonding interface, but only if the configuration is empty. The bonding interface will disappear and the slaves interfaces will be available again.
Unset. Removes the selected interface configurations.
The Bonding Interface List includes the following fields.
Name. Name configured at the bonding interface.
Alias. Identifies the interface with an alias that can be easily accessed when configuring a farm or any other service.
IP. Network-layer IP address of the bonding interface if configured. It Supports IPv4 and IPv6.
MAC. Link-layer address of the bonding interface. In case it is not configured, the bonding will inherit it from one of the slaves.
Netmask. The subnet mask of the bonding interface if configured. It must be configured at the same time as the IP Address.
Gateway. Default gateway used by the bonding interface if configured.
Status. The status of a given bonding. These are the available indicators:
- Green. It means the bonding is UP.
- Red. It means the bonding is DOWN.
Actions. The available actions for each bonding in the table are:
- Edit. Changes interface configurations like the IP address, netmask, and gateway.
- Bring down. Shuts down the interface to stop it from accepting traffic.
- Destroy. Removes the Bonding interface, but only if the configuration is empty. The bonding interface will disappear and the slaves interfaces will be available again.
- Unset. Removes interface configurations.