Overview #
Alteon is the ADC enterprise product of Radware, while DefensePro ensures security and traffic monitoring. With Radware products like Alteon, you may acknowledge its security features, the flexibility of deployment, and its support for multiple virtualizations of all Radware appliances on most virtualization platforms. But then, why do you have to rethink your choice to use another ADC? The reasons could be:
- Lack of easily accessible supportive resources.
- The lack of open-source projects to help understand the platform and its functionality.
- Delayed customer support at a time when you need it.
- Wherever your company is based, you won’t find comprehensive routes with Alteon because of its limited global coverage.
This article will guide you on how to set up RELIANOID ADC based on Radware configurations.
Prerequisites #
- A RELIANOID instance must be installed on your PC, bare-metal, virtual environment, or one must have an active ZVNcloud account. Request an evaluation for on-premise deployment.
- One must have access to the Web graphical interface. If you don’t, follow this quick Installation guide.
- One must be an active user of the Radware Alteon series and familiar with the concepts we will discuss in the section below.
- One must be able to create a virtual server in the RELIANOID load balancer. Here is a quick guide: Layer 4 and Layer 7 Virtual Server Configuration.
Basic Concepts #
Virtual Service: A virtual service is a program within Alteon ADC that a client requests access to its resources. These services include HTTP, SNMP, SSH, SIP, etc. RELIANOID has 2 types of Services, Remote and Local Services. Access these services through System >> Services.
Virtual servers: These are front-facing servers that receive all requests from the web and forward them to the corresponding services or backends. These have a VIP, Virtual Port, and Listeners. A virtual server in RELIANOID is called a Farm.
High Availability: This is the ability for a service to stay active even when the host servers or one ADC goes down. High availability is implemented by configuring a redundant copy of the master ADC and pairing it with the Master. HA in RELIANOID is achieved through a cluster. Access clusters by clicking System >> Cluster.
Server Group: Is a collection of real servers or virtual private Servers(VPS) processing client requests. A server Group is the same as Backends and is implemented through a Farm Service when using RELIANOID.
Real Servers: These are physical or VPS hosting an application. These servers are responsible for processing client requests or acting as storage for user input. A real server is called a Backend when using RELIANOID.
Health Checks: Probe signals sent to the backend servers to check for their availability or the availability of the Services. Health checks are the same as Farmguardian when using RELIANOID.
Global Traffic Redirection: Redirects traffic from various Geolocations to the closest data center. RELIANOID Implements Global Load balancing through the GSLB Farm.
Remote Logging: Used to log events that occur on the ADC to a separate storage or server. These events include problems, errors, or data on current operations. One may configure a remote logging server on RELIANOID by accessing System >> Services >> Local >> Rsyslog.
LinkProof: Used when you want to load balance between different ISPs, or routers. RELIANOID implements load balancing between ISPs through the DSLB Farm.
Example Configurations: DDoS and API Protection #
DDOS attacks are a kind that is hard to track because distinguishing legitimate and malicious traffic takes more than one strategy. To prevent your servers from being overwhelmed by a large amount of unreliable traffic, security tools like RELIANOID IPDS offer DDoS Protection through; traffic filtering, rate limiting, traffic shaping, and other various methods.
In this section, We will describe the configuration of all forms of DoS protection using RELIANOID. These configurations will base on Radware configurations.
RADWARE configurations #
Configure the Network #
- Click the Network menu item on the left sidebar.
- Click the + button to add a network.
- Assign a Name.
- Click the + button again.
- Choose your favorite Network Type, whether IPV4 or IPV6.
- Leave the Entry Type as IP Mask.
- Enter the Address and Mask for that Network.
- Click the Submit button.
Create a BDoS Profile #
- Click Network Protection >> BDoS Profiles.
- Click the + button.
- Enter a Profile Name.
- Within the Flood Protection Settings, enable all the available options.
- Within Bandwidth settings, you may limit inbound and outbound traffic bandwidth to 5000kbps.
- Within quota settings, you may limit incoming and outgoing TCP, UDP, ICMP, and IGMP settings in percentages.
- Within the Packet reporting and Trace setting, you may enable both checkboxes, packet report and packet trace.
- Click the Submit button.
Create a Network Protection Policy #
- Click Network Protection >> Network protection policies.
- Click the + button to add a policy.
- Enter a Policy Name.
- Within the classifications, choose SRC Network as any.
- Choose the DST Network as the one you created in the earlier section.
- Choose Direction as one way.
- Within the Action tab, choose the BDoS profile you already created.
- Within the Packet Reporting and Trace Setting Tab, enable Packet Reporting.
- Click the Submit button.
- Click the Update policy button beneath the menu bar.
RELIANOID Configurations #
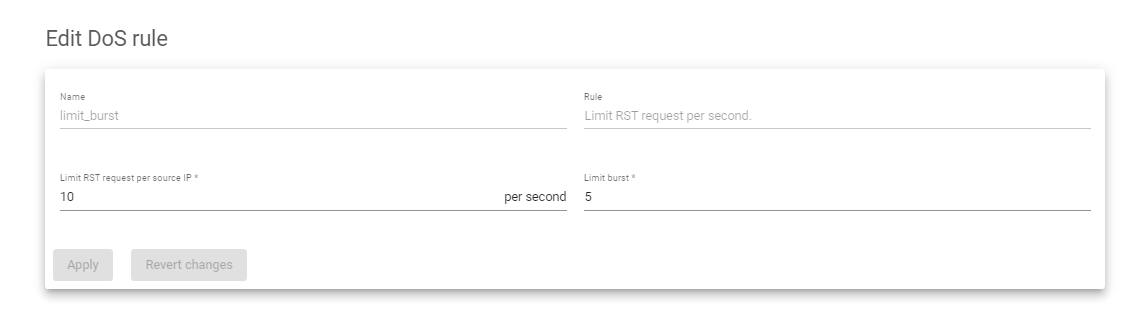
- Click IPDS >> DoS >> Create DoS rule.
- Enter a Name to Identify the Farm.
- Select a Rule from the Four preloaded rules.
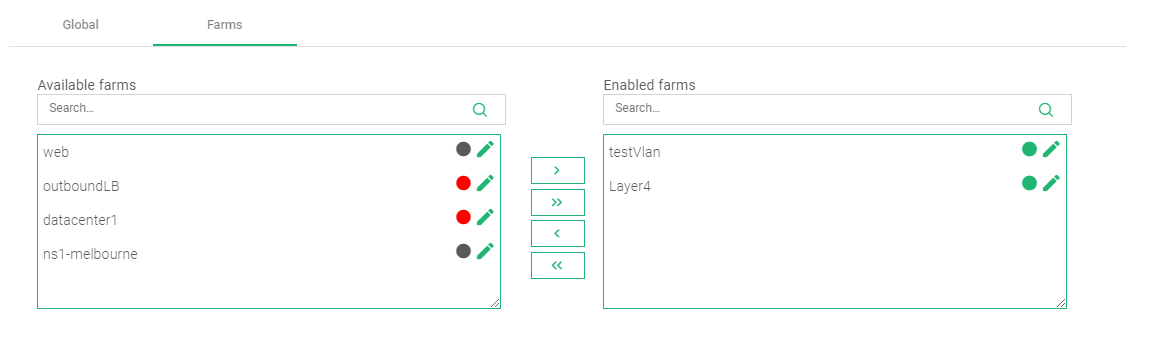
- To Apply this rule on a farm, click the Farms tab.
- Drag and Drop the farm of interest from Available Farms to Enabled Farms.
- Within the top-right corner, click the Green play button beneath the Actions section.
- Repeat the process and use all Four rules for maximum DoS mitigation.
Note:
For the rule, Total connections limit per source IP, Enter a number to limit how many connections one source IP address can have.
For the rule, Limit RST request per second, enter a number to limit the number of RST requests per source IP within a second. Limit Burst Acts as a soft limit before actual blocking happens.
For video resources, watch: Denial of Service Protection with Intrusion Prevention and Detection System in RELIANOID
Additional security configurations: Site-to-site VPN #
A site-to-site VPN (Virtual Private Network) allows organizations to connect their networks securely over the internet. This type of VPN typically connects two remote locations, like a branch office, to the headquarters network. Site-to-site VPN on RELIANOID uses protocols such as IPsec to encrypt the data transmitted between the two networks, ensuring that it is secure and private.
IPsec uses two main protocols to provide security: Authentication Header (AH) and Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP). AH provides authentication and integrity protection for IP packets, while ESP provides confidentiality, authentication, and integrity protection.
In this section, we will configure a Site-to-Site VPN with RELIANOID to ensure the security of data transmitted over the internet between two or more organizations of the same company.
For reference to the site-to-site VPN configurations from Radware, refer to this article. How to Configure a Site-to-Site VPN Tunnel Through LinkProof
Instructions: #
Create a VPN Profile #
- Click Network >> VPN >> Create VPN.
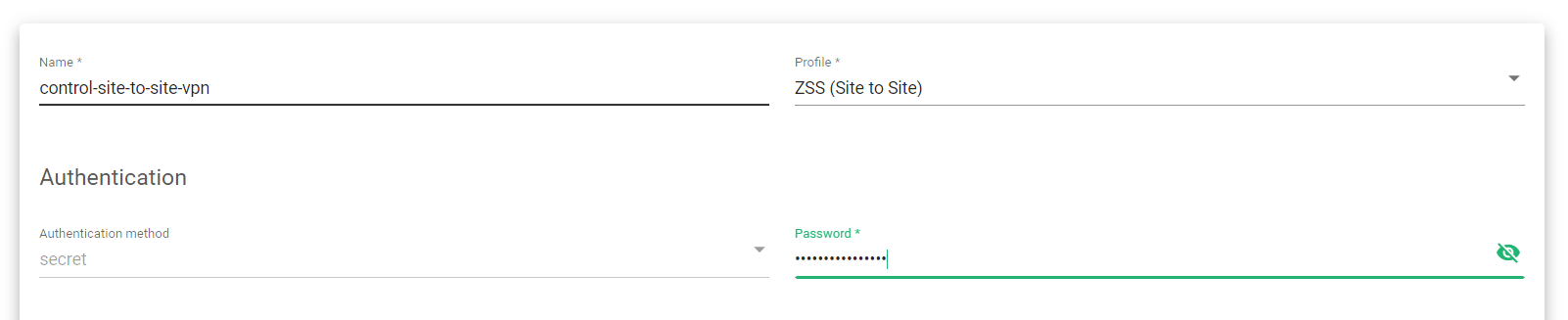
- Enter a suitable Name to Identify the VPN.
- Select the Profile ZSS(Site to Site).
- The Authentication method, by default, is a secret. Enter a strong Password to protect the VPN credentials.
Gateway configurations #
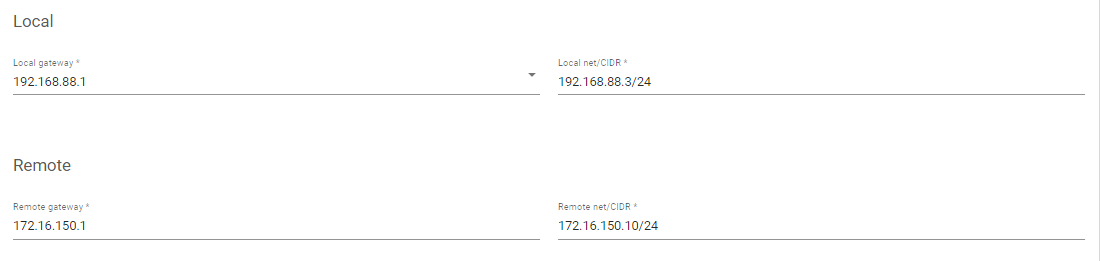
- Enter the IP address of the Local Gateway and its Local net/CIDR*
- Enter the IP address of the Remote Gateway ad its Remote net/CIDR*
IKE Phase 1 Negotiation #
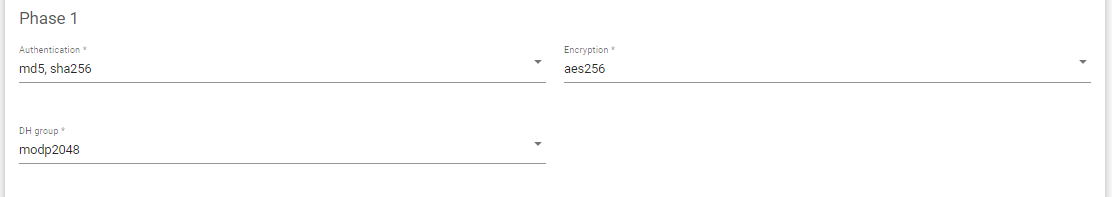
- Select the Authentication method for Phase 1.
- Select the Encryption method for phase 1 Negotiation.
- Select the DH group for the phase 1 Negotiations.
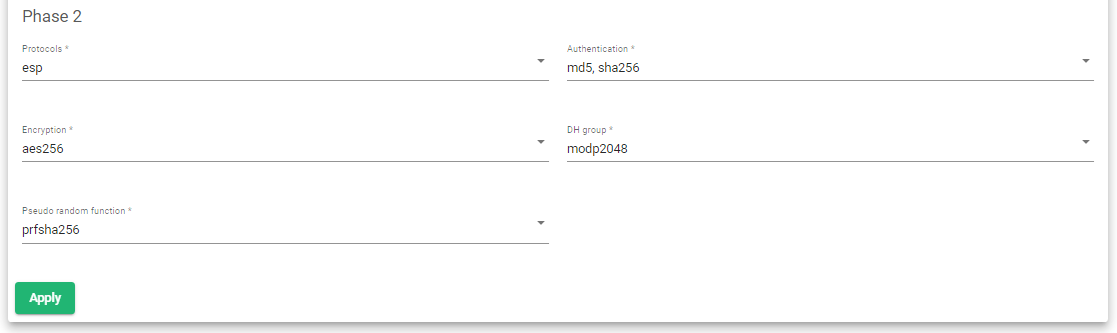
IKE Phase 2 Negotiations #
- Select phase protocol for integrity and authentication.
- Select the Authentication method.
- Select the Encryption algorithm.
- Select the Diffie-Hellman(DH group).
- Select a Random Pseudo Function to use.
- Click the Apply button to save the configurations.
Note: Ensure you make the same configurations on the Remote ADC or Datacenter branch.
Additional resources #
Web Application Firewall configuration.
Configuring SSL certificates for the load balancer.
Using the Let’s encrypt program to autogenerate an SSL certificate.
Application, Health and Network Monitoring in RELIANOID ADC.
Datalink/Uplink load balancing With RELIANOID ADC.
DNS load balancing with RELIANOID ADC.