On March 5, 2024, Meta Platforms Inc., the parent company of Facebook, Instagram, and Threads, experienced a global outage that left millions of users unable to access their accounts for approximately two hours. The incident, caused by a configuration issue, disrupted not only social interactions but also impacted Meta’s virtual reality hardware, raising concerns about the reliability and security of the tech giant’s services.
The Outage: A Brief Overview
The outage began around 10 a.m. EST, with users reporting login issues, feed refresh problems, and errors across Meta’s platforms. Even the Meta Quest virtual reality headset was affected, hindering users from progressing beyond the login interface. The disruption extended to Meta’s consumer hardware products, emphasizing the broad impact of the incident.
This outage followed a similar incident in late 2021, revealing a recurring vulnerability in Meta’s infrastructure. In 2019, the company faced its worst-ever outage, lasting over 24 hours, due to a faulty server configuration change. In conjunction with Meta’s downtime, other major platforms, including Discord and YouTube, also reported technical difficulties.
Impact on Users and Stakeholders
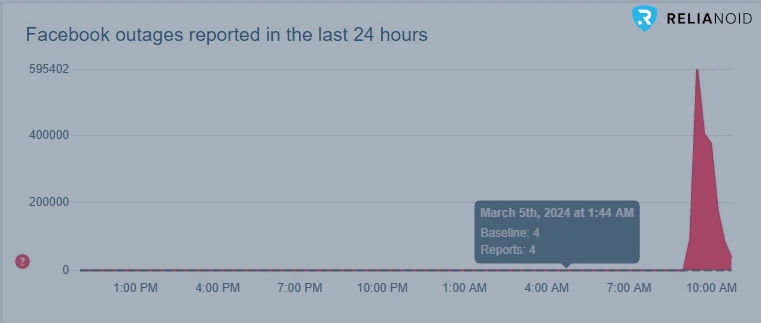
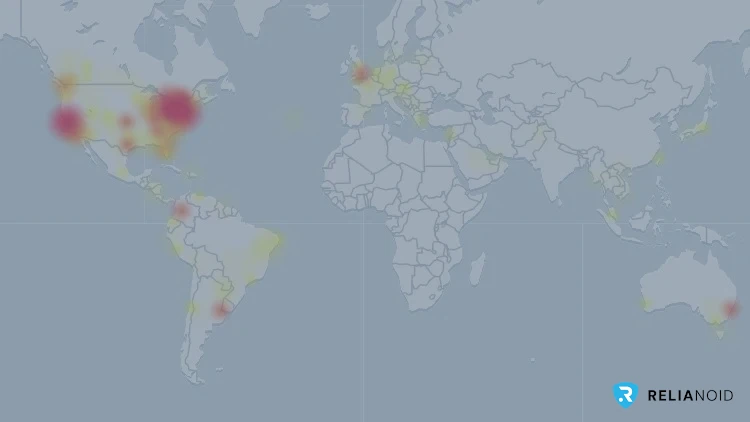
At its peak, the outage resulted in over 550,000 reports of disruptions for Facebook and about 92,000 for Instagram, according to outage tracking website Downdetector.com. The global reach of the outage underscored the dependence of users worldwide on Meta’s services for both personal and professional purposes.
Employees of Meta reported issues accessing internal work systems during the outage, causing uncertainty and concern among staff. The disruption prompted the White House National Security Council to monitor the incident, although there was no evidence of malicious cyber activity at the time.
Lessons Learned
The outage highlighted the need for secure, decentralized, and open-source social platforms. Users and industry observers alike questioned the reliability and security of Meta’s services, especially considering their track record of outages and the extensive user base affected.
1. Secure Platforms: Protecting User Privacy
Secure platforms use end-to-end encryption, safeguarding the content and metadata of messages from unauthorized access. This ensures that only the sender and receiver can read messages, enhancing user privacy and preventing third-party interference.
2. Decentralized Platforms: Resilience to Failures
Decentralized platforms, employing peer-to-peer or blockchain technologies, distribute data and functionality across multiple nodes. This mitigates the risk of a single point of failure, making platforms more resilient to outages, attacks, or censorship.
3. Open Source Platforms: Transparency and Accountability
Open-source platforms, with publicly available source code, offer transparency, accountability, and customizability. Independent experts and users can audit and verify the platform, fostering trust and reducing the likelihood of hidden vulnerabilities.
Moving Forward: The Shift Towards a More Robust Future
As users reevaluate their reliance on Meta’s platforms, the outage serves as a catalyst for the industry to prioritize the development and adoption of secure, decentralized, and open-source social platforms. Whether through user demand or industry initiatives, the lessons learned from Meta’s outage could pave the way for a more robust and resilient digital landscape. The global outage may have been a temporary disruption, but its impact on user confidence and the industry’s commitment to innovation is likely to endure.
Ready to embrace a more secure and decentralized digital experience? Join the conversation and explore alternative platforms. Contact us to learn more about the future of social connectivity. Together, let’s shape a more reliable and resilient digital world.







